SLEEP WHY IS IT SO IMPORTANT

COOPER MOHR
Content Manager
6 minutes
April 8, 2022

Sleep - why is it so important?
What physiological activity takes up the biggest part of our lives? Sleep, of course, for which we devote 25-35% of our time, which means a minimum of 25 years for the average life expectancy in the States, which is 78 years. Therefore it is surprising how little we, as well as medicine and lifestyle recommendations, attach importance to the importance of sleep for health and everyday functioning.
However, scientific achievements of recent years prove that underestimated sleep plays an important role in our well-being, joy of life, success in studies and work, immunity of the organism, and also in the risk of many diseases. Therefore, it is worth learning more about sleep and its importance for health.
What is the importance of sleep to our health?
Sleep is not simply the switching off of consciousness for a period of time. Despite the reduced activity and energy consumption during sleep, many useful biological processes take place in the brain and throughout the body. In brief, these most important phenomena are:
- organization and storage of information, getting rid of unnecessary "junk" from memory - sleep deficiency makes it difficult or even impossible to learn, explore and remember;
- reorganization and communication between nerve cells - sleep deficiency makes the work of the brain deteriorate significantly over time;
- rest and renewal of most tissues and organs of the body, as well as the production of useful amines and hormones - without sufficiently long sleep the body has no chance to regenerate, in adolescence for proper development and growth, and in later stages of life to rebuild damaged cells and accumulate energy, or "recharge the batteries".
The above processes are essential for health - without sleep our body cannot function properly.
Sleep is a complex physiological process, in which we can distinguish two fundamental, alternating stages:
- non-rapid eye movement (NREM) and
- rapid eye movement (REM).
The NREM phase, which is further divided into several stages depending on the depth of sleep, is longer and allows for rest and renewal of energy. During the much more active REM phase, the brain is more stimulated and dream formation occurs. Both stages of sleep are needed for memory consolidation and regeneration of thinking. Each sleep cycle, lasting on average about 80-120 minutes, consists of different proportions of both stages NREM and REM. For a full night's sleep we need 4-6 sleep cycles, depending on their length and genetic predisposition.
The precious influence of sleep on health and psyche has been known for a long time, but only scientific research conducted in recent years allowed us to confirm its importance in the proper functioning of the body. The consequence of sleep deficiency can be:
- lowering of cognitive abilities and concentration, difficulty in learning and remembering;
- mood disorders, anxiety, and even depression;
- weaker physical efficiency, easier fatigability, worse sports results;
- decreased immune system, increased susceptibility to infections and contagions;
- metabolic disorders leading to overweight or even obesity;
- increased risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases such as arrhythmias.
In conclusion, more serious disorders leading to long-term deficiency, as well as poor quality of sleep, can even lead to earlier death, and certainly shorten the period of life in good health and fitness.
How can sleep affect our health so widely?
It's easiest to understand the negative effects of sleeplessness on mental clarity, memory and learning ability, because probably everyone has had this experience when preparing for an exam or an urgent task at work.
In simple terms, the memorization process can be divided into 3 stages:
(a) cognitive, when we learn or experience something new,
b) consolidation, when we consolidate the memorization in the brain and
(c) recall - when we use the information stored in memory.
Sleep deprivation adversely affects all stages, including especially worsening the functioning of memory consolidation. Both long-term and short-term memory is then impaired.
Sleep and stress and condition

Sleep problems are inextricably linked to stress, mood disorders, depression and other mental illnesses. As a result of sleep phases that are too short or even skipped, the secretion of neurotransmitters and stress hormones is disrupted, resulting in impaired thinking, states of irritability and other negative emotional reactions, and increased mental health symptoms, especially in the case of already existing mental health problems. Conversely, difficulty falling asleep, waking up at night and in the morning can be an early sign of unconscious stress or even more serious mood disorders, anxiety reactions or depression - people with insomnia have a 10 times higher risk of this serious condition.
Thus, sleep problems may be both one of the causes of mental problems and one of the symptoms and aggravating factors of such ailments. What's more, statistically, men who sleep 4-5 hours have the same testosterone levels as men ten years older.
Sleep in athletes
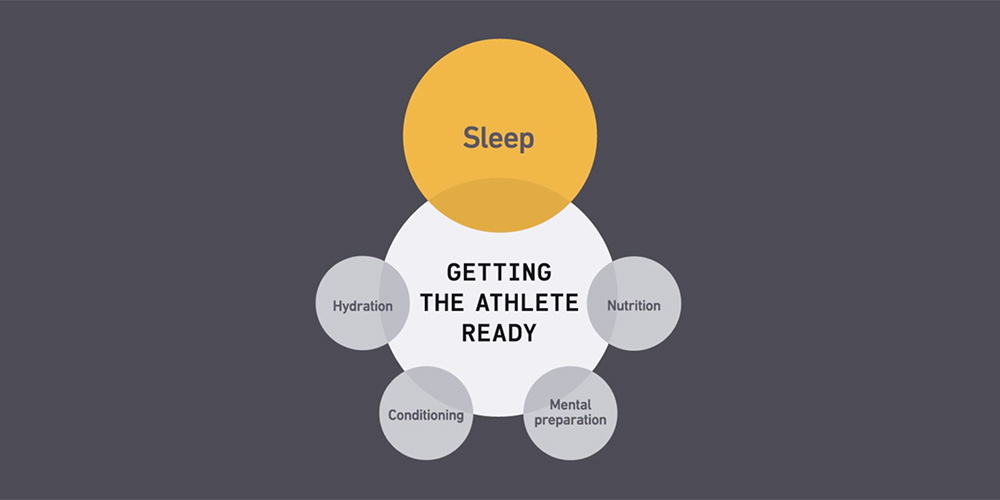
Adequate sleep determines good physical condition and performance, of which all professional athletes know. Practically all of these areas influenced by sleep are important for physical and psychical performance, which is equally important for sports competition.
Sleep deprivation results in, among other things, deterioration of motor coordination, faster fatigue as a result of abnormal metabolic functions, longer reaction times and often an increased risk of injury, as well as extended time needed for rest and recovery after exercise. Sleep is important not only for athletes, but for anyone who cares about an active lifestyle, as the health-promoting effects of fitness club exercise or recreational jogging can simply be hindered or abolished by sleep deficiencies.
Proper sleep has a significant positive impact on the immune system, and a lack or deficiency of sleep results in lowered immunity. Studies have shown that with sleep deprivation, the number of defensive Th1 lymphocytes decreases and inflammatory cytokines increase. As a result, our resistance to infections and infestations decreases, and even the beneficial effect of vaccinations, such as against influenza, worsens. Sleep also helps with other natural defenses of the body, such as fever. As we know, the temperature rises in the afternoon and evening and at night, and during infections we sleep a lot, so the body has a chance to fight the infection.
Sleep deprivation and chronic diseases
When sleep is lacking, this fight against pathogens is hindered. Persistent sleep deprivation can permanently damage the immune system, dramatically reducing the level of immune cells NK (Natural Killer, responsible for destroying cancer cells and those infected with viruses) and causing symptoms of chronic inflammation, manifested among others by an increase in the level of C-reactive protein (inflammatory marker). This is associated with an increased risk of diabetes, heart disease or cancer.
The increased risk of serious chronic diseases becomes one of the key arguments for the importance of sleep for health. People who sleep too little or suffer from insomnia, as well as more serious diseases such as obstructive sleep apnea, are more likely to be overweight and obese, have high blood pressure and other heart diseases, including arrhythmias. There is strong evidence that sleep deficiency along with overweight are important factors in the development of type 2 diabetes (so-called insulin-dependent diabetes, occurring mainly in adults), and improving sleep quality may improve treatment outcomes, including achieving normalization of blood sugar levels.
Additionally, people with abnormal sleep cycles, such as shift workers, have been observed to have an increased risk of certain cancers: breast cancer in women or prostate cancer in men. More research is needed on the relationship of sleep and chronic disease risk to determine what is cause and what is effect, but regardless, it appears that lack of proper sleep is important in their development and effectiveness of treatment.
Several research reports have found increased mortality in individuals who sleep less than 6 hours per night, have difficulty falling asleep, or experience inadequate recovery during sleep.
Sleep disorders
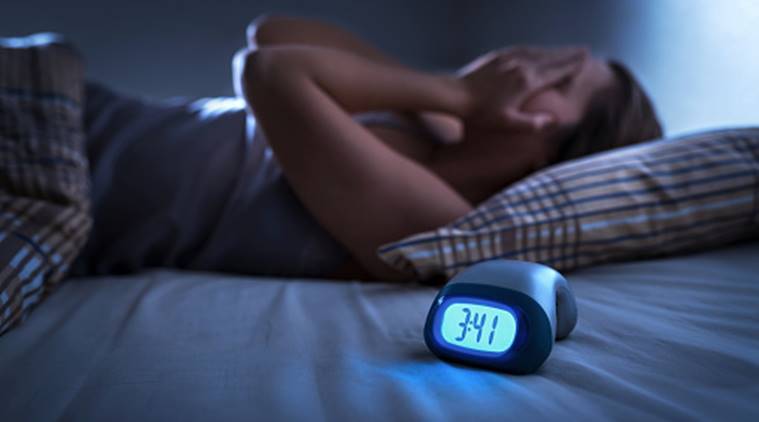

There are several types of sleep disorders, ranging from fairly mild to severe, even life-threatening. The most common problem is insomnia - an estimated 50-70 million, or one in three American adults, have sleep problems. Comparing this scale to the Polish population, it can be assumed that 7-8 million Poles suffer from chronic or periodic sleep deficiency.
Insomnia is characterized by difficulty falling asleep and/or inability to maintain adequate sleep length, e.g. waking up in the middle of the night or in the morning and having a long break or staying awake until getting out of bed. The causes of insomnia can be many: from temporary stress or anxiety reactions, already described mental problems or illnesses, to symptoms resulting from other medical conditions or the effects of certain medications. Bad habits are also a frequent cause, such as excessive exposure in the evening to blue light (smartphone or laptop screen), late meals, drinking alcohol or coffee, lack of exercise, or such simple matters as inadequate place and conditions for sleeping (high bedroom temperature, uncomfortable bed), etc.
Important in terms of serious consequences is the so-called obstructive sleep apnea. This is a relatively common disease, especially in obese men, still rarely diagnosed. It is characterized by snoring, unconscious periods of apnea occurring during sleep, leading to hypoxia of the brain and profound disturbances of the sleep phases, resulting in lack of rest and recovery after the night. The causes of sleep apnea are most often anatomical and require specialized treatment.
Whatever the cause, insomnia impairs quality of life, productivity at work, and increases risk of disease, so it requires intervention, and often medical attention and specialized therapy. But first, it is useful to confirm the evaluation of our sleep to verify if we have too little and of what quality. It is assumed that the desired length of sleep per day varies according to age:
- school children (5-12 years) - 9-12 hours;
- teenagers (13-17 years) - 8-10 hours;
- adults (18-64 years) - 7-9 hours;
- seniors (over 65) - 7-8 hours.

I wonder how many of us manage to sleep that long on a regular basis. In addition, it is important for the quality of sleep to fall asleep within 15-20 minutes of going to bed, to have no prolonged interruptions during sleep, and to wake up spontaneously rather than being pulled out by an alarm clock in the middle of a sleep phase. Daytime naps, or so-called siestas, although evaluated positively, do not count towards total sleep length. To assess sleep length and quality, a diary can be kept over a period of time to note key data that will be helpful in planning behavioral improvement and possible treatment of insomnia.
You might also be interested in these

8 minutes
The liver is particularly important for maintaining normal blood glucose levels. It is where excess glucose is stored, in the form of glycogen, among other things.

Carmelita Claus
Content Manager
8 minutes
IF diet is becoming more and more popular. It raises many controversies among dietetic experts.

COOPER MOHR
Content Manager
5 minutes
There are regenerative processes in every organism that form the basis for maintaining health and preventing disease.

Carmelita Claus
Content Manager
.svg)





